Part 1: 5G – The Final Frontier of The Connected World

The blog is the first installment of a three-part blog series that will be talking about Telecom & 5G network in the current ecosystem, the significant impact of Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Augmented & Virtual Reality on telecoms’ performance and the transitional introduction to Metaverse. Furthermore, this Blog series will try to encapsulate the essence of technology and its marvelous ways of adaptation to fit the requirements of the evolution ICT is currently going through.
A Foreword by 4G
“If everything seems under control, you’re not going fast enough.”- these golden words of Mario Andretti define the essence of universal functioning in connectivity space. Once the world stopped resisting and saw how staying connected happened via technology while every other traditional way of “staying in touch” failed, the “Need for speed” became the most important area of focus in the current connectivity domain. As we grow and expand our roots in the post-pandemic era the clarity of our requirement to stay connected becomes the deciding factor in our chance at ultimate connectivity. The move from 4G to a 5G network is the answer to an evolved demand by the telecom ecology. 5G is designed to offer higher data speeds, ultra-low latency, higher reliability, massive network capacity, increased availability, and a more uniform yet new user experience offered to existing and new industries.
5G: The Promise land
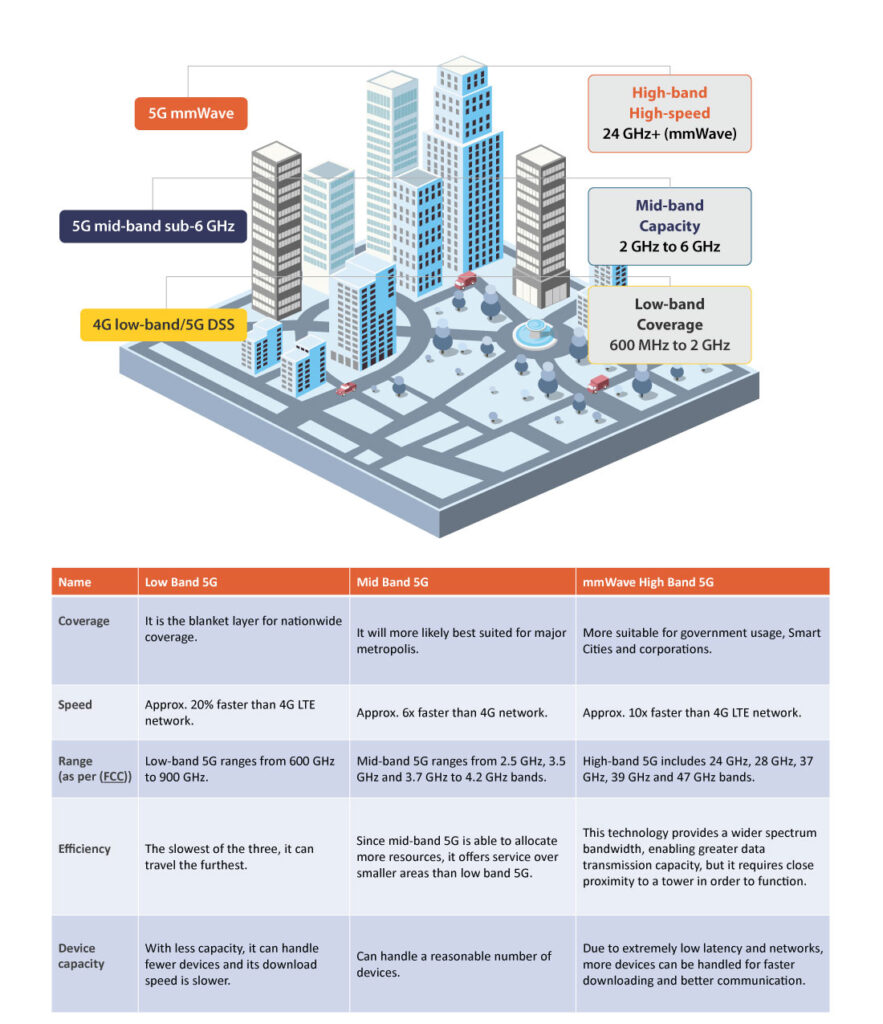
The 5G Network: The 5G networking architecture consists of three different network types with the following characteristics:
How Did 5G Win Over its Captious Critics?
The most important 6 factors that impressed quibbling network cynics include:
- Speed: 5G is faster on IoT devices and offers speed of download to aid generic downloads of movies, videos, and music as well as automation, online meetings, calls, etc.
- Latency: 5G has low latency allowing the network to aid AI, VR, and IoT, as well as open multiple web pages without putting pressure on the device.
- Capacity: 5G delivers up to 100x more capacity than 4G delivering greater performance even while users are shifting between cellular and wireless strategies.
- Bandwidth: 5G offers greater bandwidth than 4G aiding in faster data transfer- effective on any IoT device in use.
- Data Access: 5G has an upper hand while accessing important data because of its speed and bandwidth thus there is less to no tower congestion
- Innovation: 5G technology is not only aiding innovation, but it’s also paving paths to connect to a wider range of devices including drones and sensors. This eventually will empower IoTs to assist users in more ways of effective functioning.
From Consuming to Creating
Given the existing VoIP technologies over an existing data network, this fifth generation of cellular telephony surprised the fourth generation (LTE or Long-Term Evolution) by showing its distinct independence from a particular voice network. A key component of 5G is that the networks should be able to anticipate the needs of each application. By incorporating dynamic considerations, 5G becomes more of an operational technology than just a consumer technology.
Telephony, for example, is no longer dependent on a provider. The invention of VoIP itself was a breakthrough. Unlike a traditional phone network, it was designed to act as a phone network without needing voice components. In the present day, VoIP calls are bridged to traditional phone lines. Not only do we have many VoIP companies but also those that offer video over the Internet. Programmers (or toolkit developers) can create such applications using open APIs. Despite the usage of the term “consumer technology”, customers/consumers can create and contribute to technology. –
As devices become more intelligent, networks are becoming more intelligent. After the development of 5G-enabled devices, 5G seems more like the past and not the future of networking. Using 5G to move functionality from devices to providers’ networks will land in some conflict or other- outgrown technology will give birth to more advancements inbuilt into devices. This vicious never-ending cycle has been the way of networking- it still is, and it always will be.
5G’s Pedantic Approach: Pushing Users Towards a world beyond!
An infrastructure that rewards innovation and honors all the stages of a solution’s lifecycle ensures technical development isn’t stunted in the evolution process. While 5G has found its audience due to its reliability and latency features. With different bands of 5G handling certain requirements its elemental that both networks and devices get to take advantage of the technology especially when there is a critical requirement or enterprises are pressed for time- something dependable makes it easier to stay focused.
Factors Working Against 5G’s Chop Logic
The specious argumentation of 5G as a network, becomes a topic of discussion because it’s too early in the development of the technology to put all your bets in one bag- which hasn’t even been through enough scrutiny to achieve perfection in any aspect yet marketed as a flawless service offering. Factors worthy of further discussion include:
- Fallacious Upload speeds: 5G may promise high download speeds, but the upload speeds never reach more than 100 Mbps.
- Security: As attackers try to exploit vulnerabilities, enterprise exposure to threats increases because of the sheer number of devices a 5G network can accommodate.
- Lack of encryption: Tech to protect assets has advanced but are we ready to overlook the standard of hackers? Tech and hacking techniques both are growing exponentially. 5G may have high speed and low latency to make it look like a dream- too good to true- but the network lacks encryption at least against precision attacks.
- Cost: The infrastructure setup cost and maintenance of 5G is higher than other networks.
The good thing about 5G is that it handles extremely well when needed for something critical. As a technology, 5G is now going into so many different sectors that we will be placing these technology elements in both the networks and the devices so they can take advantage of these technologies. The majority of what we have heard so far suggests that 5G isn’t just a consumer-focused technology, and it goes beyond the norm of the basic ask from a network, more suited to be termed as an “operational technology”.
An Extraordinary Voyage into the Future: 3GPP Standardization Keeping 5G Company
The 3GPP, or 3rd Generation Partnership Project, is a major body of the telco industry that produces standards for wireless cellular networks. The phase definition for networks by 3GPP is as follows:
- Stage 1: To introduce the first use scenarios for the new services and applications, along with related (new) system architecture requirements.
- Stage 2: Modifications are made to different protocol components, messages, and architectural components on the lower (ISO/OSI layer) level. Depending on the requirements, new architectural blocks may be needed to accommodate new requirements.
- Stage 3: To make the new services available through the enhanced system architecture, the communication protocols, and messages at the upper layers of the protocol stacks are further enhanced.
5G technology has entered the third phase and made its way down into lower-tier segments, such as 5G enabled wearable devices and AR glasses. Can you imagine what these 5G devices will enable?
Humans as a race have only dreamt of intelligent devices – progressively enriching our experiences every step of the way. That’s us- a curious bunch pushing boundaries, harnessing potential out of thin air, and exploring the scope of human problems treated and solved as technical challenges. AI is delivering enhanced experiences; Machine Learning is using data to offer relatable interactions while Augmented and Virtual Reality make the net of the network seem more real than most of our realities. These factors are molding the face of perception, logical reasoning, and fundamentals of interaction. We are moving on and away from 5G’s ubiquitous influence while the technology is still being figured out. Anyways who needs to resolve the problems with 5G while the next solution is ready to rise on the horizon?
Please stay tune with us for Part 2 of this blog series which will be published soon.
Related Posts
The Global Scenario Of 5G Adoption In Telecom Industry
Troubleshoot Your Fraud Management Solution To Battle 5G Fraud Concerns
The Role Of Cloud-Based IMS In The Growth Of 5G Network